Latest News
European countries’ online casino legislation: which are the strictest and most lenient countries?

Gambling laws are changing all the time and it can be difficult to keep up. Most of Europe allows some form of gambling but the rules and legislation are different from one country to the next. In this guide, we’re looking at the strictest and most lenient countries in Europe when it comes to gambling.
While some countries strictly legislate and provide licences to some gambling companies (but not to all that apply for licensing) other countries have a much more liberal approach. A more competitive industry allowing for competition means consumers can find more bonuses and promotions.
Norway – strict
Norwegian gambling is strictly restricted and regulated through sites that are state approved, such as Norsk Tipping. However, Norwegian people are free to use companies that are technically based in other countries – so in reality, there isn’t a huge impact on the consumer. Lots of options exist for the Norwegian market and sites such as Casinospesialisten.net can help you through your options.
Cyprus – strict
Cyprus has some of the strictest rules, and you cannot bet online on horse races or dog racing. Spread betting is not permitted, and you may not use cryptocurrency in your gambling in the country. This means there are some limited sportsbooks but that is the main extent of gambling services in Cyprus.
Cyprus is actually one of the few European countries that bans certain types of gambling, and most of Europe has more liberal rules.
Germany – strict (but changing)
Germany has some complicated laws regarding gambling, but they are changing all the time. In 2021, a new Interstate Treaty aligned all the states in the applicable restrictions and their ability to provide licences. Previously, each state had its own specific rules.
The treaty means there are sports betting licences and a lot of different markets as well as online casinos, but there is still a different method for each state when it comes to providing betting shops and other land-based gambling outlets.
Some forms of gambling are limited and you can only bet a certain amount. Slots are capped at a “per-spin” rate to prevent people from gambling too much in one go, and bookmakers can’t provide as many markets as some other countries.
Sweden – lenient
Sweden’s laws have changed significantly but the government runs most of the online gaming industry, which means they can get more income from taxes. Swedish players may be at a disadvantage as a result, due to the fact there isn’t the same level of competition between gambling companies. Also, the companies don’t have the same requirement to provide customer service, for instance.
Offshore gambling isn’t necessarily illegal and a lot of people use casinos based in Malta.
Malta – lenient
Though this may be one of the smallest countries on the list, Malta has become a global gaming powerhouse due to the fact that they have very lenient laws when it comes to gambling.
Everything from narrative-driven slots to sportsbook gambling is legal in the country, with a number of countries’ gambling markets turning to offshore solutions in Malta.
The Malta Gaming Authority has jurisdiction and provides two different types of licence: B2B and B2C.
With B2B licences, the product should be for business use, which means that people need this sort of licence to produce casino games or make other related framework and payment services for the market.
B2C is more relevant to the consumer, such as traditional bookmakers and sportsbook markets, and online gambling companies offering casino games.
Malta generates 12% of its GDP from the online casino and gaming industry, which shows what an incredibly large part it plays in the culture of the island.
Finland – lenient
The government runs three organisations: Veikkaus, Fintoto and RAY. These have control over the different aspects of gambling, including lotteries and sports (Veikkaus), land-based casinos (Fintoto) and horse racing (RAY).
Finland’s Lotteries Act requires that all gambling companies be licensed by the state but that doesn’t mean Finnish people can’t choose to gamble elsewhere with offshore accounts, if they so wish.
United Kingdom – lenient
The UK has lenient laws that are controlled by the Gambling Commission (UKGC).
The UKGC regulates an incredible range of gambling, including over 800 different sportsbooks. Laws are regularly enforced, and gambling companies have to act on issues such as problem gambling. One of the most lenient aspects is that you don’t get taxed on any of your winnings – no matter the size of the gambling win, you won’t pay tax on it in the United Kingdom.
Conclusion
The world of casino legislation is constantly evolving, and it is important to keep up to date with the latest regulations in your country. However, many countries allow for offshore gambling where the consumers interact with gaming companies that are based elsewhere, though these may have to stick to regulations, too. European countries often have lenient casino and gambling laws when compared to other countries around the world.
-

 eSports5 hours ago
eSports5 hours agoTEAM VITALITY AND PARIS SAINT-GERMAIN ESPORTS ANNOUNCE EA FC COLLABORATION
-

 Asia7 days ago
Asia7 days agoTesla to showcase Model Y with NODWIN Gaming at the thrilling BGMS Season 4 Grand Finals
-

 Compliance Updates7 days ago
Compliance Updates7 days agoSOFTSWISS Compliance Expert Shares Knowledge on AML in iGaming for Sumsub Academy
-

 Africa7 days ago
Africa7 days agoRacing1 is exhibiting for the first time at the Grand Prix D’Afrique
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoÅland-Based Gaming Company Paf Becomes Main Partner of the Finnish Ski Association – One of the Most Significant Sponsorship Agreements in the Association’s History
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoAnimo Studios debuts virtual hosts for live table games starting with Stake
-
 Latest News7 days ago
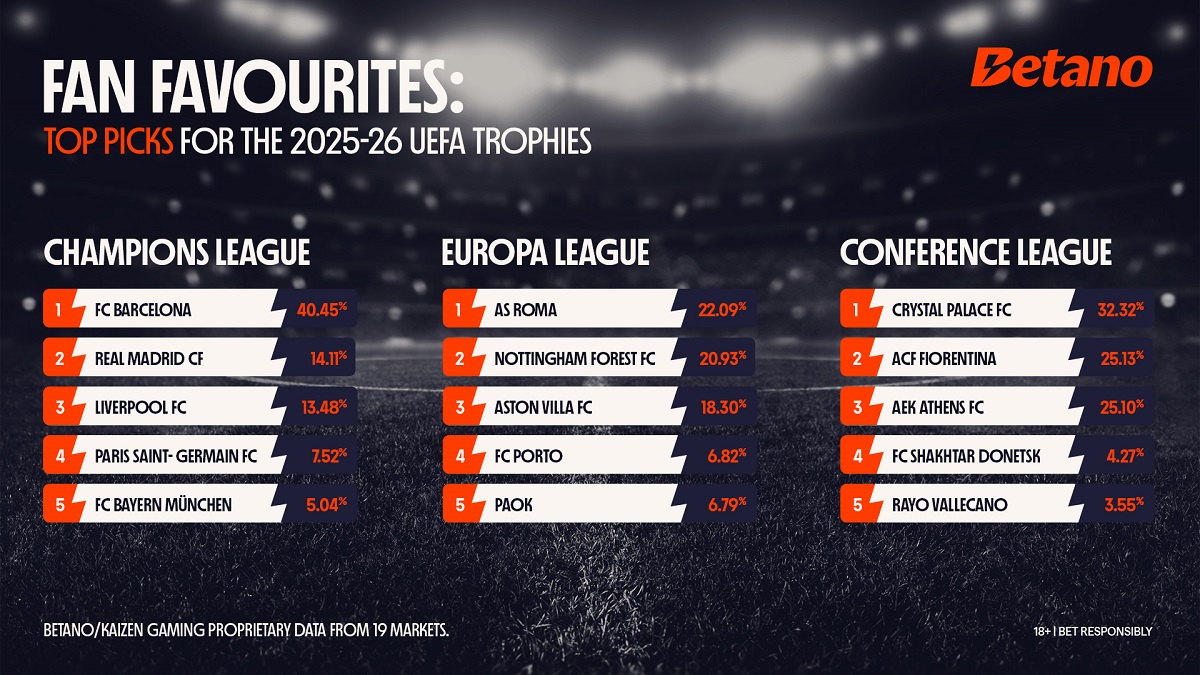
Latest News7 days agoKaizen Gaming data – FC Barcelona the fan favourite to win the Champions League
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoWeek 37/2025 slot games releases